
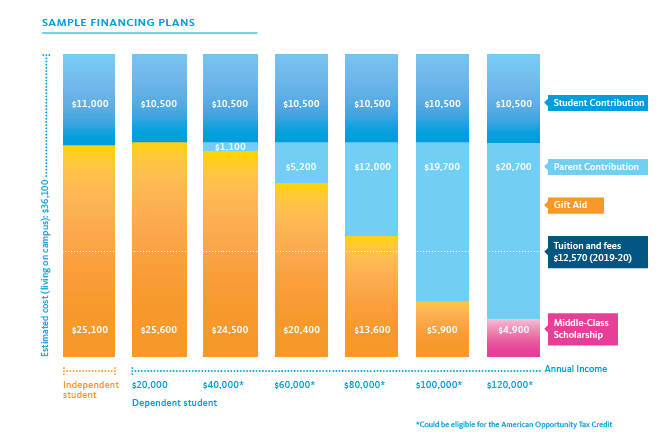
The enrollment rate measures the level of education in primary schools in developing nations. The enrollment rate has increased by more than 45% and dropped out rates have significantly declined, from 61% down to 16% between 1976 and 2020. Some education policies have been successful while others have not. This study presents a framework for evaluating progress in primary education in developing countries.
Multidisciplinary training
Interdisciplinary training can be beneficial for primary teachers. This approach supports the integration of knowledge and skill from various disciplines and allows students to develop professional creativity. It can be a complex process that involves answering large questions, researching issues and problems, as well as solving problems from different perspectives. There are many methods to incorporate interdisciplinary perspectives into the classroom.
Interdisciplinary training can be implemented with existing funding mechanisms. The main problem is how to evaluate the effectiveness of such programs. Interdisciplinary training programs have few data on their outcomes. Unfortunately, this problem is not unique to interdisciplinary training.
Common core competencies
Teachers who wish to help children in their early years develop the skills necessary to succeed in school, work, and at home can use the common core competencies in primary teaching. There are many similarities between the core competencies at both the state and national levels. These guidelines can be used by educators to help them design professional development plans.
The framework was developed after extensive research on teaching practices. It was created to help teachers identify and prioritize the essential teaching and learning skills. It provides tips on teaching and assessing transferable skills. The framework is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Curriculum
The Ministry of Education, Culture and Sport (MECS) is responsible for the management of educational institutions within the country, as well as abroad. The ministry also oversees the curriculum and establishes the objectives for each stage. These objectives are a guideline for what students should know and how they can apply the knowledge to their learning. The curriculum defines the student's ability solve complex problems and to apply the knowledge from each stage.
Spain's primary education curriculum is obligatory. It does not contain specific Social Science aims. It includes a list of "General Objectives for Primary Education", and "Evaluation Criteria". These standards are well-constructed and easily measurable. Teachers must assess the standards during each lesson. This limits the education's ability to be flexible and adapt to new ideas.
Framework for Learning
Implementing the Framework for Learning in Primary Education can help you develop the skills your students need to be successful in school. Each stage builds upon the one before. This framework lists the stages and steps for each stage. It also includes tools to assess and evaluate progress.
Frameworks are an essential part of teaching and learning because they enable educators to align curriculum activities and goals to achieve those goals. Frameworks also assist teachers in creating motivating learning environments and integrating assessment into the lessons. A framework helps teachers see how they are united in a shared vision. This makes it easy for parents to share this vision.
FAQ
What is the purpose of schooling or education?
Education should help students develop skills necessary for employment. It is not only a pursuit of academic excellence, but also a social activity, where children can share their knowledge and gain confidence from one another through activities like music, art, and sports. It is all about teaching students how to think critically, and how to create so they can be independent and self-reliant. What does it mean to have good educational standards?
High educational standards ensure that every pupil achieves their potential. These standards provide clear guidelines for teachers to follow with their students. Good education standards allow schools to be flexible enough for changing needs. In addition, they must be fair and equitable: every child has the same chance of success regardless of his/her background.
Homeschooling is for everyone.
Anyone can homeschool. No special qualifications are required.
High school graduates are qualified to teach their children. In fact, many families choose to teach their older children while they attend college.
Parents can teach their children even if they have not received formal education.
After satisfying certain requirements, parents can become certified teachers. These requirements vary by state.
Some states require that all homeschooled students pass a test before they graduate. Others do not.
Homeschooling parents must register their family with the local school district.
The process involves filling up paperwork and submitting the completed form to your school board.
After registering, parents will be able to enroll their child in either public or privately-funded schools.
Some states permit parents to homeschool their children without having them registered with the government.
If you live within one of these states, it is your responsibility to ensure that your children fulfill the state's mandatory attendance law.
What is the difference between public and private schools?
All students can attend the public school for no cost. They provide education for students from kindergarten through highschool. Private schools charge tuition fees. They offer education from preschool to college.
There are also charter schools, which are publicly funded but privately run. Charter schools are not bound by traditional curricula. Instead, they give their students more freedom to learn what interests them.
Charter schools are popular with parents who believe their children should receive quality education regardless of their financial status.
What does it mean for a teacher to teach early childhood education?
Special training is required for teachers in early childhood education. Most states require applicants for teaching positions to have certification from the state board before they are allowed to work in public school.
Some states require that teachers pass exams on reading and math.
Some states require that teachers have completed a minimum number of courses related to early childhood education.
Many states have minimum requirements for teachers. However, these requirements vary widely between states.
Should I be a specialist or branch out in one area?
Many students choose to concentrate on one subject (e.g. English History and Math) rather that branching into several subjects. It's not necessary to be a specialist. For instance, if your goal is to become a doctor you can choose to focus in either surgery or inner medicine. You could also opt to become a general physician, specializing in either pediatrics, family practice or psychiatry. You could focus on sales, marketing, finance, research, and management if you are interested in a career in business. The decision is up to you.
Do you think it is difficult to be a teacher
It takes a lot of commitment to become a teacher. You will need time to study.
You should expect to work around 40 hours per week while pursuing your degree.
You will also need to find a job that suits your schedule. Many students report having trouble finding part-time jobs that allow them to balance their schedules with schoolwork.
If you get a permanent job, you'll likely be teaching classes during the workday. You might even be required to travel to other schools throughout the week.
How do I select my major?
Students choose their majors depending on their interests. Because they find it easier to study something they love, some students choose to major on a subject that they really enjoy. Some students want to go into a field where there is no job. Still, others choose a major because they hope to earn money during their studies. Whatever your reasons may be, you should consider what job you might enjoy after graduation.
There are many methods to learn more about the different fields of study. Talk to your friends and family about their experiences in these fields. To find out if there are jobs available, you can read newspapers and magazines. Ask your guidance counselor about possible career options. Visit your community center or library to find out more about Career Services. Check out books related to various topics at your library. You can search the Internet for information about specific careers.
Statistics
- Think of the rhetorical power of nineteenth-century abolitionist Harriet Beecher Stowe, Martin Luther King, Jr., or Occupy Wall Street activists with their rallying cry of “we are the 99 percent.” (bostonreview.net)
- These institutions can vary according to different contexts.[83] (en.wikipedia.org)
- They are also 25% more likely to graduate from high school and have higher math and reading scores, with fewer behavioral problems,” according to research at the University of Tennessee. (habitatbroward.org)
- “Children of homeowners are 116% more likely to graduate from college than children of renters of the same age, race, and income. (habitatbroward.org)
- And, within ten years of graduation, 44.1 percent of 1993 humanities graduates had written to public officials, compared to 30.1 percent of STEM majors. (bostonreview.net)
External Links
How To
What is vocational education?
Vocational education prepares students for the workforce after high school. Students are trained in specific skills to be able to do a particular job such as welding. Vocational Education also offers apprenticeship programs that provide on-the-job training. Vocational education is distinct from general education as it focuses more on training individuals for specific jobs than on learning broad knowledge that can be used in the future. Vocational training is not designed to prepare individuals for university but rather to assist them in finding jobs upon graduation.
Vocational education can take place at all levels of schooling. This includes primary schools, secondary schools and colleges, universities as well as colleges, technical institutes, technical colleges, trade schools, community college, junior colleges, four-year colleges, and colleges. There are also many specialty schools like nursing schools and law schools, legal schools, medical schools and dental schools as well as veterinary medicine, veterinary medicine, firefighting, police academies and military academies. Many of these provide both academic instruction and practical experience.
Over the last decade, several countries have made significant investment in vocational education. The effectiveness of vocational education is still controversial. Some critics say it does not improve students' employability. Other argue that it prepares them well for life beyond school.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics 47% of American adults have a postsecondary certificate. This figure is higher for those with more education. 71% (25-29) of Americans have a bachelor's level or higher and work in fields that require a postsecondary degree.
According to the BLS in 2012, almost half of Americans had at the least one type of postsecondary credential. A third of Americans have a two-year associate's degree and 10% hold a four year bachelor's degree. One out of five Americans held a master's degree or doctorate.
The median annual wage for individuals with a bachelor's in 2013 was $50,000. This was compared to $23,800 when they had no degree. The median salary for people with advanced degrees was $81,300.
The median wage for people who did not finish high school was only $15,000. Those with less than a high school diploma earned $13,000 per year.